Story Of King David 1010 BC to 970 BC:
{2nd Book Of Samuel}
The Story Of King David, a biblical figure who ruled as the second king of Israel, from around 1010 BCE to 970 BCE. He is revered in Jewish, Christian, and Islamic traditions as a prophet, warrior, and poet.
David was born in Bethlehem and became a shepherd as a young boy. He was anointed by the prophet Samuel to be the future king of Israel while still a youth, and he gained fame for his victory over the Philistine giant Goliath. After Saul, the first king of Israel, died in battle, David was anointed as king by the tribe of Judah, and he eventually united all of the tribes of Israel under his rule.
David is known for his military successes, including his conquest of Jerusalem, which he made his capital city. He also established a strong central government and reformed the religious practices of the Israelites. David is credited with writing many of the psalms in the Book of Psalms, and he is remembered as a skilled musician and poet.
However, David was also known for his personal flaws, including his adultery with Bathsheba and his role in the death of her husband, Uriah. Despite these shortcomings, David is remembered as one of the greatest kings of Israel and an important figure in the history of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.

970 BC to 931 BC: King Solomon:
{2nd Book Of Chronicles}
King Solomon was a biblical figure who ruled as the third king of Israel, from around 970 BCE to 931 BCE. He is known for his wisdom, wealth, and building projects, including the construction of the First Temple in Jerusalem.
Solomon was the son of King David and Bathsheba, and he inherited the throne after his father’s death. He was known for his wisdom and justice, and he is credited with authoring many of the proverbs in the Book of Proverbs. Solomon’s wealth and power made him a respected and influential figure in the ancient world, and he is said to have had diplomatic relations with other kingdoms, including the Queen of Sheba.
One of Solomon’s most famous accomplishments was the building of the First Temple in Jerusalem, which became the center of Jewish worship. He also built a palace complex and other important structures in Jerusalem. In addition to his building projects, Solomon was also known for his love of learning and his patronage of the arts.
However, Solomon’s reign was not without controversy. He is said to have married many foreign wives, which went against Jewish law and led to the worship of foreign gods in Israel. After his death, the kingdom of Israel split into two, with the northern kingdom of Israel and the southern kingdom of Judah each ruled by different kings.
Despite his flaws, Solomon is remembered as a wise and powerful king, and he is an important figure in the history of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
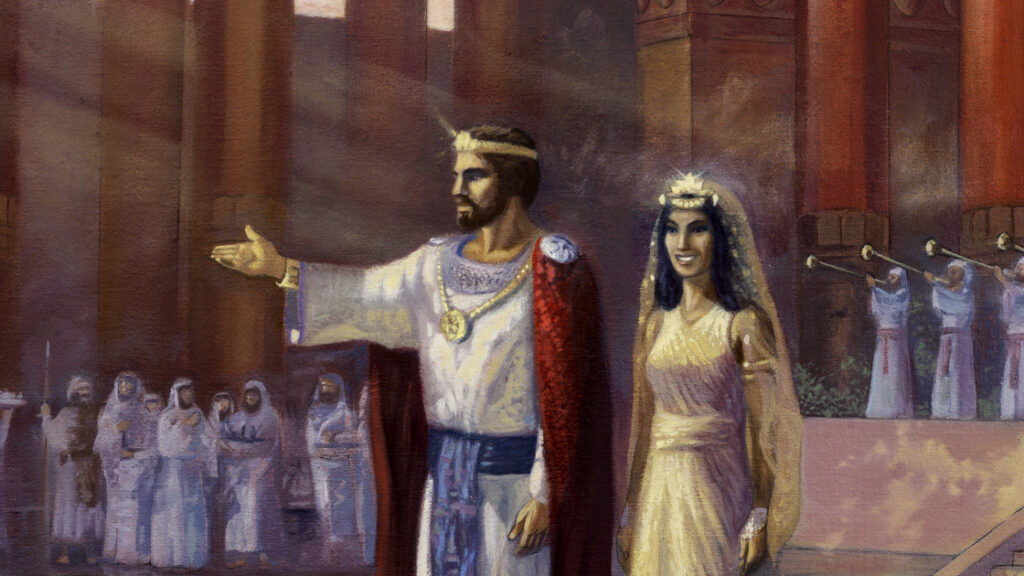

Queen Of Sheba
Queen Of The South
The Queen of Sheba, also known as the Queen of Saba, is a figure from ancient history and legend. She is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the Christian Old Testament, and the Islamic Quran, and she is known for her wealth, wisdom, and visit to King Solomon.
According to the biblical account, the Queen of Sheba was a ruler of a kingdom located in the area of modern-day Ethiopia and Yemen. She heard of the fame and wisdom of King Solomon of Israel and traveled to Jerusalem to meet him and test his wisdom. She brought with her a great retinue and many gifts, including gold, spices, and precious stones.
The meeting between the Queen of Sheba and King Solomon is described in the Bible as a great exchange of knowledge and wealth. The Queen was impressed by Solomon’s wisdom and the grandeur of his kingdom, while Solomon was pleased with the Queen’s gifts and her recognition of his greatness. According to some legends, the Queen of Sheba became a convert to Judaism, while others suggest that she returned to her kingdom and continued to rule there.
The Queen of Sheba has been celebrated in art, literature, and music for centuries. Her story has inspired many interpretations and adaptations, and she is often depicted as a symbol of wisdom, power, and beauty. In Ethiopian tradition, she is identified as the Queen of the South, and she is said to be the mother of Menelik I, the founder of the Solomonic dynasty of Ethiopia.